Introduction
This page provides guidance on how to code the technical stuff so that you can access the information without having to go to the site. This is a brief overview of the CKAN API, demonstrating some example API calls.
To fully utilise the API, some general programming skills are helpful, but not essential.
API Tokens
Before you get started, you will want to create yourself an API Token. An API Token is a means of identifying yourself to the site when you make API calls, and you will need to supply this for the majority of API calls in order to pass permission checks for the action you're attempting to perform.
Creating API Tokens
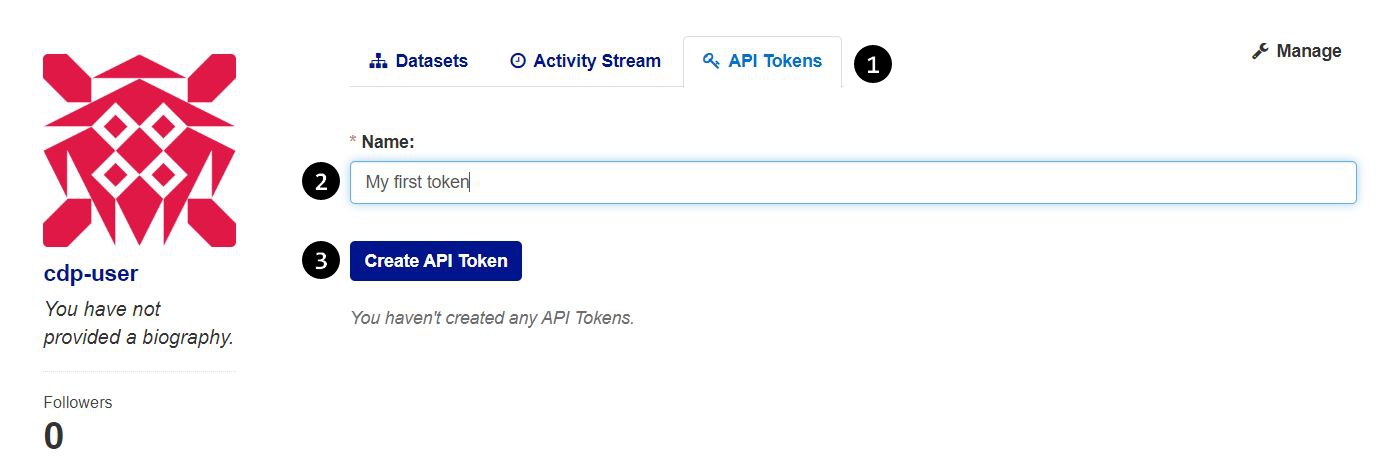
Log in to your account, and then go to your user profile by clicking the "My User Profile" link in the sidebar of your dashboard, or by clicking "User Profile" in the small dropdown that appears by hovering over your username in the top right of the page. From there:
- Click the "API Tokens" tab in the page.
- Enter a name for your new API Token in the "Name" field.
- Click the "Create API Token button".
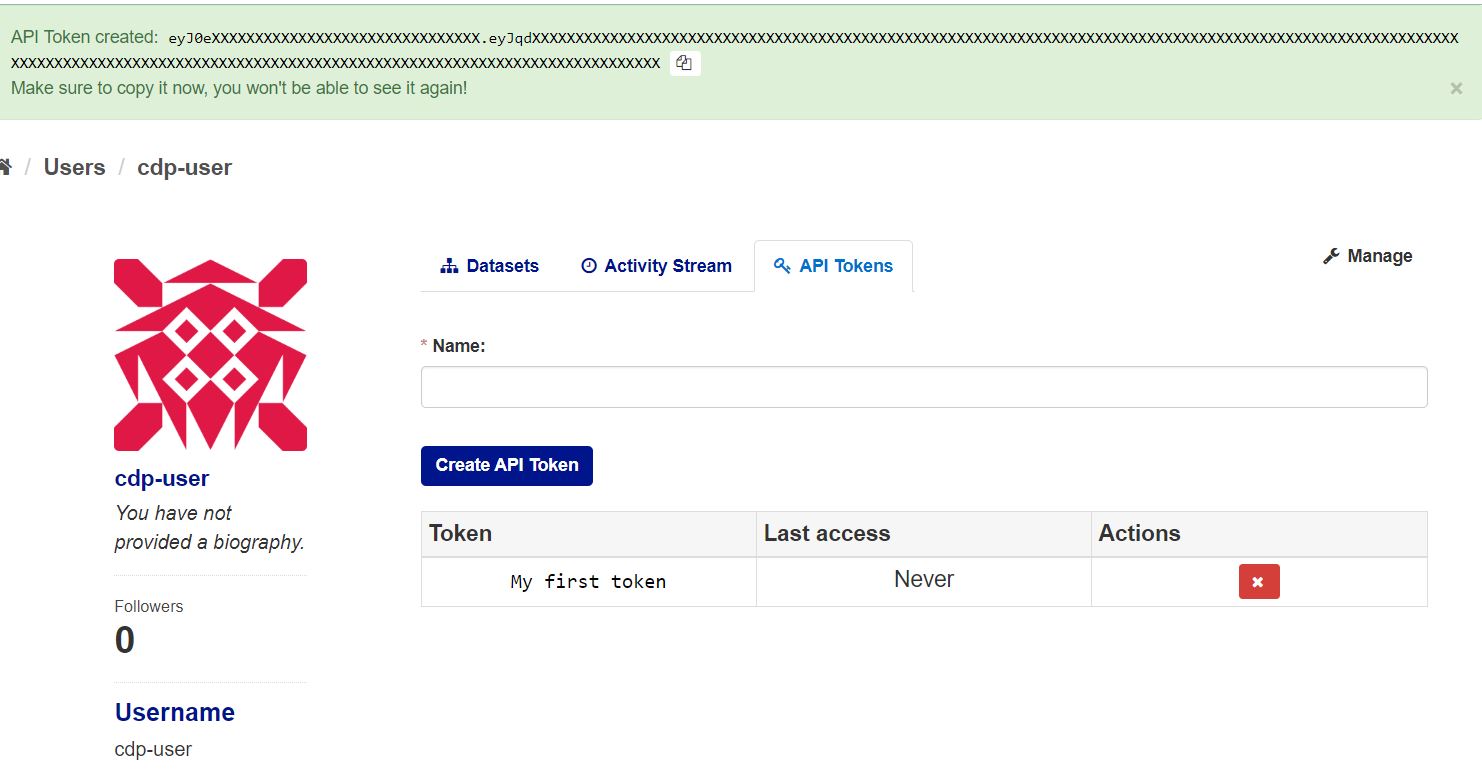
Once you have done this, the page will refresh and a notice at the top of the page will tell you what your new API Token is. It will be a very long string of alphanumeric characters. You will only ever be shown your API Token this one time, so you'll need to copy the token value and keep it somewhere safe so you can refer to it later.
Using API Tokens
via Postman
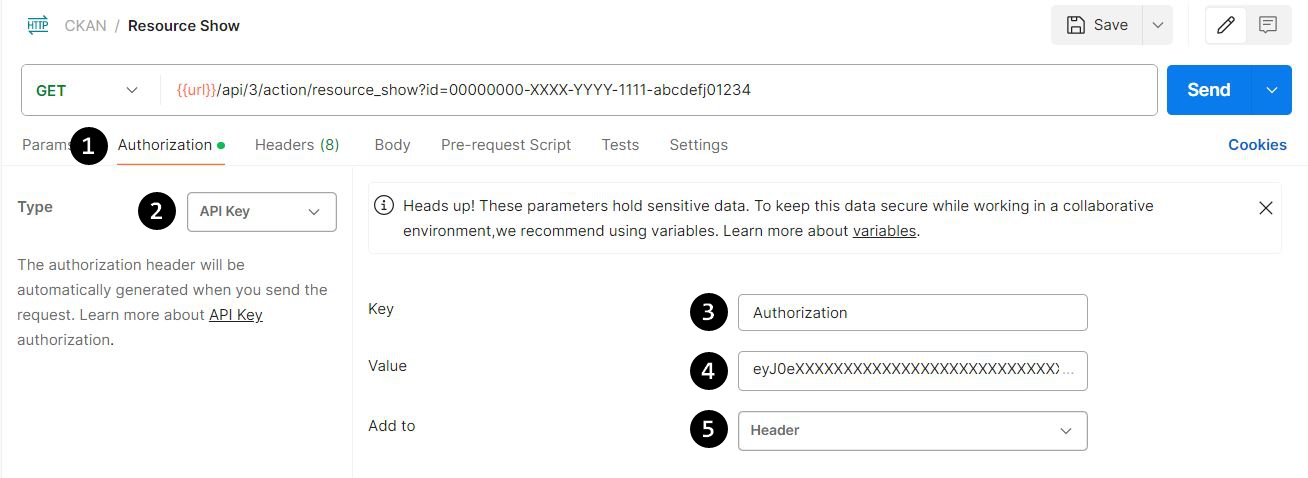
To identify yourself when making an API call, you'll need to supply your API Token in the Authorization HTTP header of your request. If you're using Postman (or other GUI equivalent) to make API calls, then the easiest way to set this up is by doing the following:
- Click the "Authorization" tab in your request's settings.
- Set the Type of authorization to "API Key".
- Make sure the Key field has a value of "Authorization".
- Enter your API Token in the Value field.
- Make sure the Add to field is set to "Header" select option.
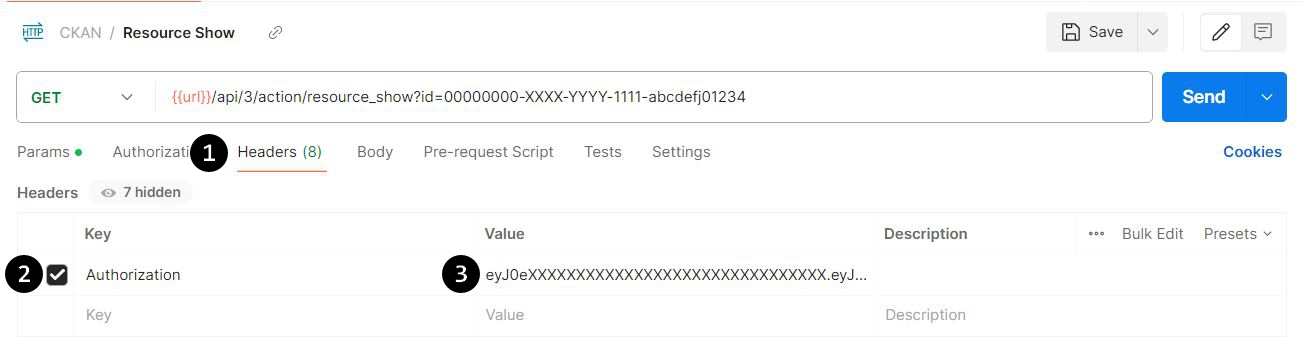
As an alternative, you can manually add in the Authorization header by doing the following steps (in the screenshot, generated headers have been hidden). Note that if you're manually adding in this Authorization header, you will want to set the Type in the "Authorization" tab to "No Auth", so that your manual header doesn't conflict with anything that Postman tries to set up for you.
- Click the "Headers" tab in your request's settings.
- In the empty row at the bottom of the Headers table, click the cell with the placeholder "Key", and then type in the value "Authorization".
- Then, click the cell with the placeholder "Value" to the right of it, and enter your API Token.
via cURL
If you are using cURL to send API requests, you can supply your API Token by making use of the -H option to define the Authorization header. An example of what this looks like is as follows.
curl -H "Authorization: eyJ0eXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX.eyJqdXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX" https://connecteddata.nationalgrid.co.uk/api/3/action/resource_show?id=00000000-XXXX-YYYY-1111-abcdefj01234
Forgotten/Lost API Tokens
If you forget or lose your API Token, you can create a new one to replace it. If you are sure that the forgotten API Token isn't being used by anyone else, or by any scripts or services that you rely on, then it's generally safer to delete it rather than leaving it active. You can delete an API Token by clicking the red "X" (revoke) button in its row in the API Tokens table in your user profile.
Example API calls
The base URL for the calls is: https://connecteddata.nationalgrid.co.uk/api/3/action/
Here are some examples of using the API to get data from the portal:
The above just scratches the surface. There are hundreds of calls for getting data from the portal. These are documented here docs.ckan.org/en/latest/api/index.html. Scrolling through the API documentation will give you a better idea of how to extract what you need.
Python 3.8 Example
This example gets all the packages, finds the embedded capacity register package and pulls the names and ids of the resources.
Simple Python Example using NGED CKAN API
#import the necessary libraries
import urllib3
import json
import pprint
#Allows for arbitrary requests while transparently keeping track of necessary connection pools for you.
http = urllib3.PoolManager()
#Get the data
response = http.request('GET','https://connecteddata.nationalgrid.co.uk/api/3/action/package_list')
# Use the json module to load CKAN's response into a dictionary.
response_dict = json.loads(response.data)
# Get the list of packages
print(response_dict['result'])
['constraint-management-zone-cmz-polygons', 'constraint-management-zone-cmz-postcode', 'distribution-substation-location-easting-northings', 'electric-vehicle-capacity-map', 'embedded-capacity-register', 'flexdgrid-fault-level-monitor-data', 'generation-capacity-register', 'green-recovery-map', 'live-data', 'primary-substation-location-easting-northings', 'time-to-connect', 'time-to-quote', 'transformer-detail-for-the-south-west-licence-area', 'western-power-distribution-south-west-grid-supply-point-demand', 'wpd-network-capacity-map']
# Get the list if resources for each package
for package in response_dict['result']:
#loops until it finds the embedded capacity register
if package == 'embedded-capacity-register':
#gets the resources
response = http.request('GET','https://connecteddata.nationalgrid.co.uk/api/3/action/package_show',{'id': package})
#converts to json
response_dict = json.loads(response.data)
#loop through the response to get the resource id and name
for resource in (response_dict['result']['resources']):
print('resource_name=',resource['name'],'\nresource_id=',resource['id'])
resource_name= Embedded Capacity Register - December 2020
resource_id= 7f4e46db-0dcb-449e-8842-f5f585370e4a
resource_name= Embedded Capacity Register - February 2021
resource_id= 50609de1-9484-41e5-82e6-dfa5b2287759
resource_name= Embedded Capacity Register January 2021
resource_id= d4270bb9-59e4-403d-ad8f-1c382c10963f
cURLs
"Integrate this dataset using cURL" section at the bottom of dataset pages.
You can get the metadata and a list of resources of a dataset by the following

Dataset id

Reource id

You can download the resource file by

